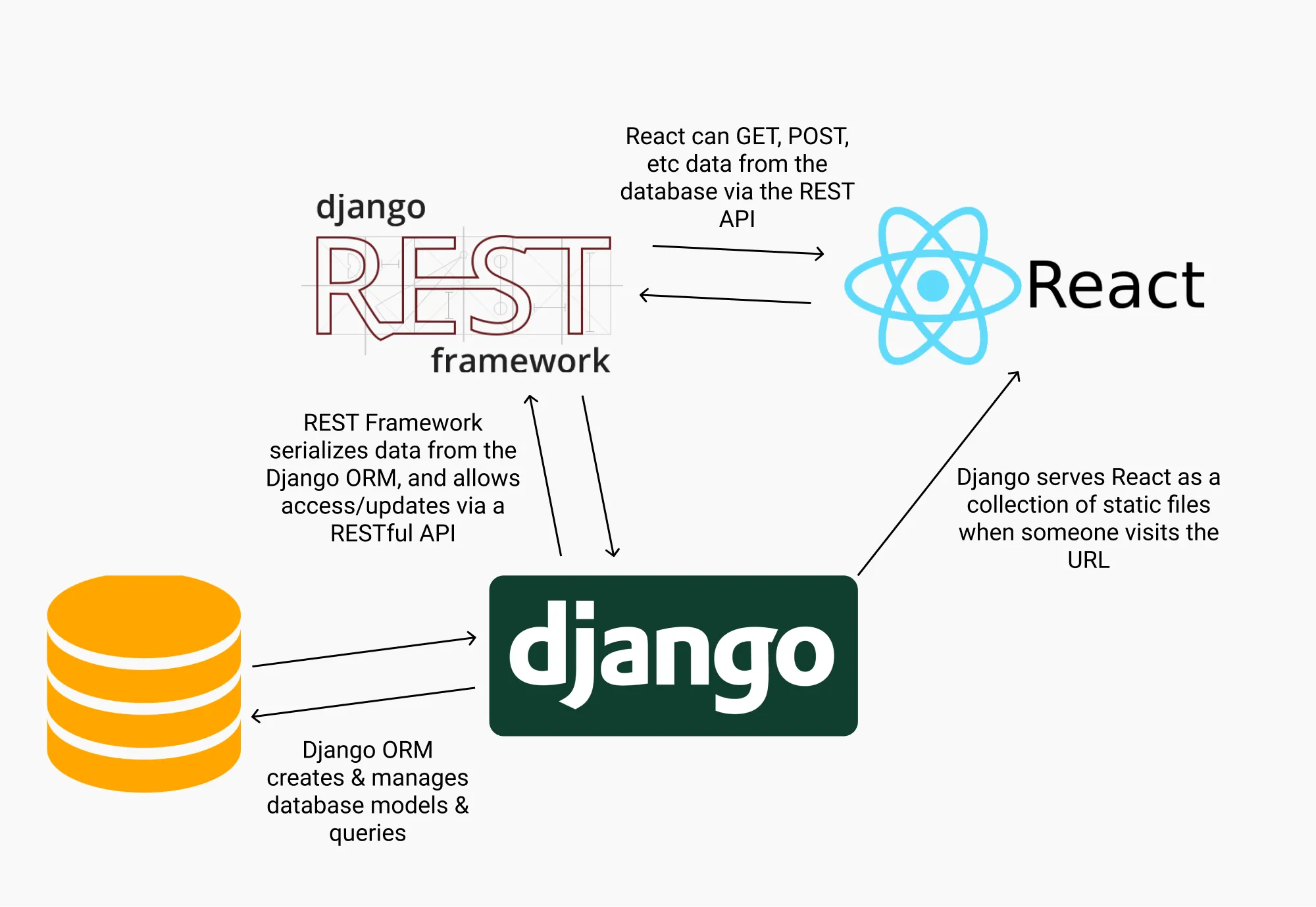
Quick Introduction
Jargons
- API: Application Programming Interface is a shorthand way to describe how two computers communicate directly with one another.
- REST: REpresentational State Transfer
- ASGI: Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface
- WSGI: Web Server Gateway Interface
- CORS: Cross-Origin Resource Sharing is a mechanism that lets web pages access resources from other domains.
- CSRF: Cross-Site Request Forgery is a malicious exploit that tricks a user’s browser into performing unwanted actions on a trusted website. It’s also known as XSRF.
Web APIs
For example, the following url https://zhengyuan.xin/api/ has three components:
- Scheme:
https - Hostname:
zhengyuan.xin - (Optional) Path:
/api/
HTTP Verbs
| CRUD | HTTP Verbs |
|---|
| Create | POST |
| Read | GET |
| Update | PUT |
| Delete | DELETE |
Request/Response
1
2
3
4
| Request/Response Line
Headers
(Optional) Body
|
Status Code
- 2XX: Success
- 3XX: Redirection
- 4XX: Client Error
- 5XX: Server Error
DRF
Serializer
- Complex datatypes (querysets or model instances) serialize into Python datatypes (then converted into JSON/XML).
- Incoming JSON/XML data unserialize into Python objects.
There are two types of view, function-based and class-based.
Function-based Views
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| from rest_framework.decorators import api_view, throttle_classes
from rest_framework.throttling import UserRateThrottle
class OncePerDayUserThrottle(UserRateThrottle):
rate = '1/day'
@api_view(['GET', 'POST'])
@throttle_classes([OncePerDayUserThrottle])
def view(request):
return Response({"message": "Hello for today! See you tomorrow!"})
|
Use decorators to wrap your function-based views to ensure they receive DRF’s Request instances.
Class-based Views
Views
APIView
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import authentication, permissions
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class ListUsers(APIView):
authentication_classes = [authentication.TokenAuthentication]
permission_classes = [permissions.IsAdminUser]
def get(self, request, format=None):
"""
Return a list of all users.
"""
usernames = [user.username for user in User.objects.all()]
return Response(usernames)
|
APIView is the base class in DRF- Handler methods:
get(), post(), put(), delete()- receives
request, which is DRF’s Request instance, not Django’s HttpRequest. - returns DRF’s
Response instance, not Django’s HttpResponse instance.
- Full control over the request handling process.
- Source code: views.py, decorators.py
Generic Views
GenericAPIView
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from myapp.models import MyModel
from myapp.serializers import MyModelSerializer
class MyGenericAPIView(GenericAPIView):
queryset = MyModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = MyModelSerializer
def get(self, request):
serializer = self.get_serializer(self.get_queryset(), many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
|
- Subclass of
APIView - Add support for
queryset for database queries. - Add support for
serializer_class to determine which serializer to use. - Built-in support for Pagination, Filtering, and Ordering.
- Source code: generics.py, mixins.py
Mixin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.mixins import ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin
from myapp.models import MyModel
from myapp.serializers import MyModelSerializer
class MyMixinView(ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin, GenericAPIView):
queryset = MyModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = MyModelSerializer
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs)
|
Mixins are used with GenericAPIView and they provide actions rather than handler methods- Common mixins:
CreateModelMixin => .list()ListModelMixin => .create()RetrieveModelMixin => .retrieve()UpdateModelMixin => .update() and .partial_update()DestroyModelMixin => .destroy()
CreateAPIViewListAPIViewRetrieveAPIViewDestroyAPIViewUpdateAPIViewListCreateAPIViewRetrieveUpdateAPIViewRetrieveDestroyAPIViewRetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView
ViewSets
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| # views.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404
from myapps.serializers import UserSerializer
from rest_framework import viewsets
from rest_framework.response import Response
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ViewSet):
"""
A simple ViewSet for listing or retrieving users.
"""
def list(self, request):
queryset = User.objects.all()
serializer = UserSerializer(queryset, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
def retrieve(self, request, pk=None):
queryset = User.objects.all()
user = get_object_or_404(queryset, pk=pk)
serializer = UserSerializer(user)
return Response(serializer.data)
# urls.py
from myapp.views import UserViewSet
from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter
router = DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', UserViewSet, basename='user')
urlpatterns = router.urls
|
ViewSet provide actions rather than handler methods