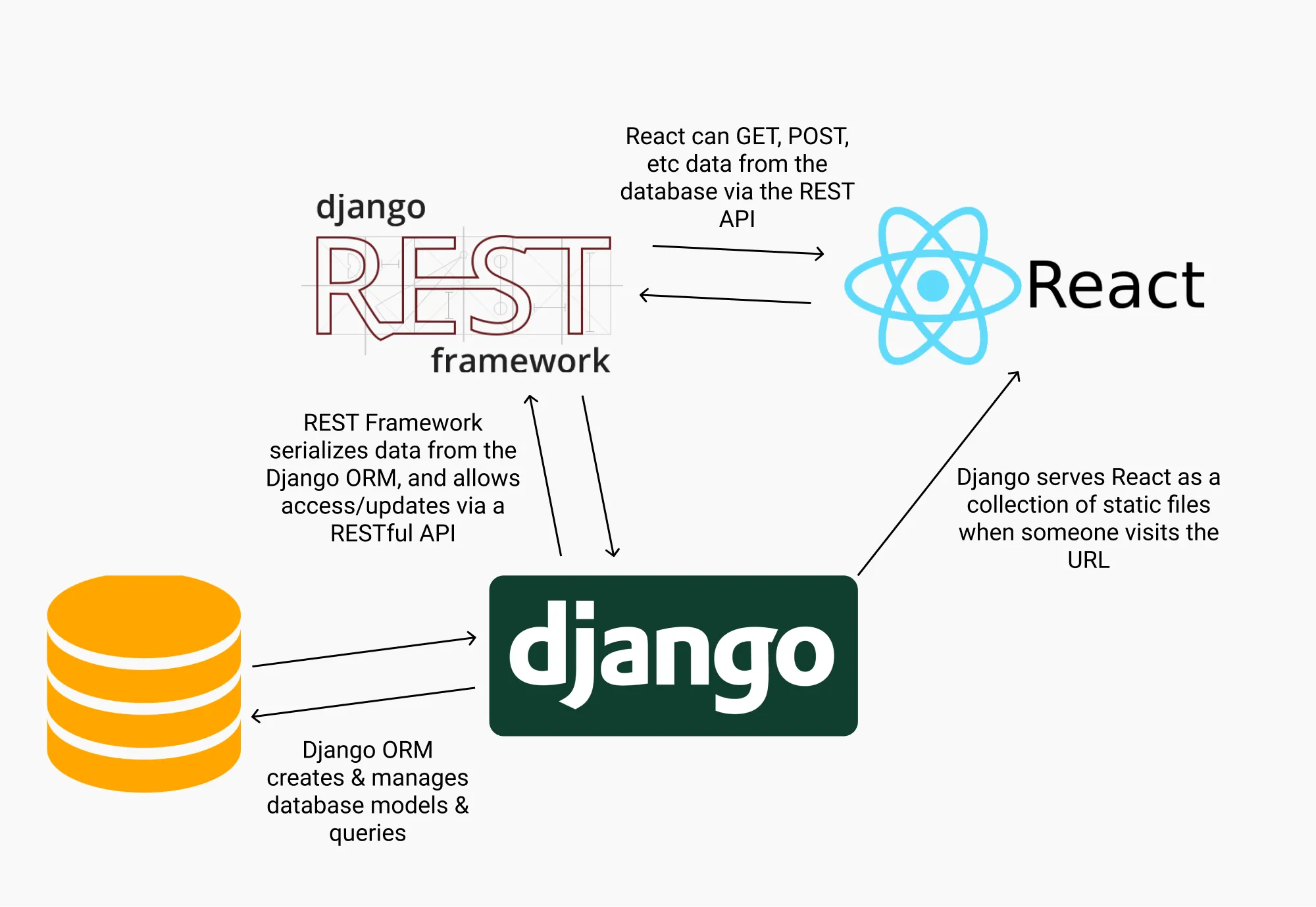
Django MVT (Model-View-Template)
Model
- Represents the data layer of the application.
- Defines the structure of the database, including tables, fields, and relationships.
- Handles data storage, retrieval, and validation.
- Interacts with the database using Django’s ORM (Object-Relational Mapper).
Define Relationships
Many-to-Many
Should be defined on either side of the relationship using ManyToManyField(). (Notice that Category was passed as a string, because the class Category was not defined yet. Django uses a string representation and it’s considered the best practice.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # One product can belongs to many categories, such as bread -> food & on_sale_product
# One category can also has many products, such as food -> bread & chicken
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
categories = models.ManyToManyField('Category')
class Category(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
|
Many-to-One
Should be defined on the many side of the relationship using ForeignKey()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| class Order(models.Model):
order_number = models.CharField(max_length=50)
customer = models.ForeignKey('Customer', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
class Customer(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
|
The kwarg: related_name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# Case 1
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
author = models.ForeignKey('Author', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
author = Author.objects.all(name='Zheng Yuan')
books = author.book_set.all()
# Default method <class_lowercase>_set
# Case 2
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
author = models.ForeignKey('Author',
related_name='books',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
books = author.books.all()
# Now, the method now becomes the value of related_name
|
One-to-One
Should be defined on either side of the relationship using OneToOneField()
View
- Acts as the business logic layer.
- Processes user requests, interacts with the Model to fetch or manipulate data, and prepares the data for rendering.
- Returns a (Django’s)
HttpResponse, often by rendering a template with the processed data. - In Django, views are typically Python functions or classes.
Template
- Represents the presentation layer.
- Defines how the data is displayed to the user.
- Uses Django’s template language to dynamically generate HTML by combining static content with data from the View.
- Separates the design (HTML/CSS) from the logic (Python code).
Django REST Framework
Serializer
- Complex datatypes (querysets or model instances) serialize into Python datatypes (then converted into JSON/XML).
- Incoming JSON/XML data unserialize into Python objects.
View
APIView (Class-based)
- Returns a (DRF’s)
Response - Handler methods:
get(), post(), put(), delete(), etc. - Full control over the request handling process.
- views.py, decorators.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import status
class MyAPIView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
data = {"message": "This is a GET request"}
return Response(data, status=status.HTTP_200_OK)
def post(self, request):
data = {"message": "This is a POST request"}
return Response(data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
|
Function-based
@api_view()- API policy decorator
- View schema decorator
GenericAPIView
- Subclass of
APIView - Add support for
queryset for database queries. - Add support for
serializer_class to determine which serializer to use. - Built-in support for Pagination, Filtering, and Ordering.
- generics.py, mixins.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from myapp.models import MyModel
from myapp.serializers import MyModelSerializer
class MyGenericAPIView(GenericAPIView):
queryset = MyModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = MyModelSerializer
def get(self, request):
serializer = self.get_serializer(self.get_queryset(), many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
|
Mixin
- Mixins are used with
GenericAPIView and they provide actions rather than handler methods - Common mixins:
- CreateModelMixin:
.list() - ListModelMixin:
.create() - RetrieveModelMixin:
.retrieve() - UpdateModelMixin:
.update() and .partial_update() - DestroyModelMixin:
.destroy()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.mixins import ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin
from myapp.models import MyModel
from myapp.serializers import MyModelSerializer
class MyMixinView(ListModelMixin, CreateModelMixin, GenericAPIView):
queryset = MyModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = MyModelSerializer
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs)
|
ViewSets
- A type of class-based view which provides actions rather than
handler methods - Bound to the corresponding actions at the point of finalizing the view using
.as_view() - Register the viewset with a router class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404
from myapps.serializers import UserSerializer
from rest_framework import viewsets
from rest_framework.response import Response
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ViewSet):
"""
A simple ViewSet for listing or retrieving users.
"""
def list(self, request):
queryset = User.objects.all()
serializer = UserSerializer(queryset, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
def retrieve(self, request, pk=None):
queryset = User.objects.all()
user = get_object_or_404(queryset, pk=pk)
serializer = UserSerializer(user)
return Response(serializer.data)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| from myapp.views import UserViewSet
from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter
router = DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', UserViewSet, basename='user')
urlpatterns = router.urls
|