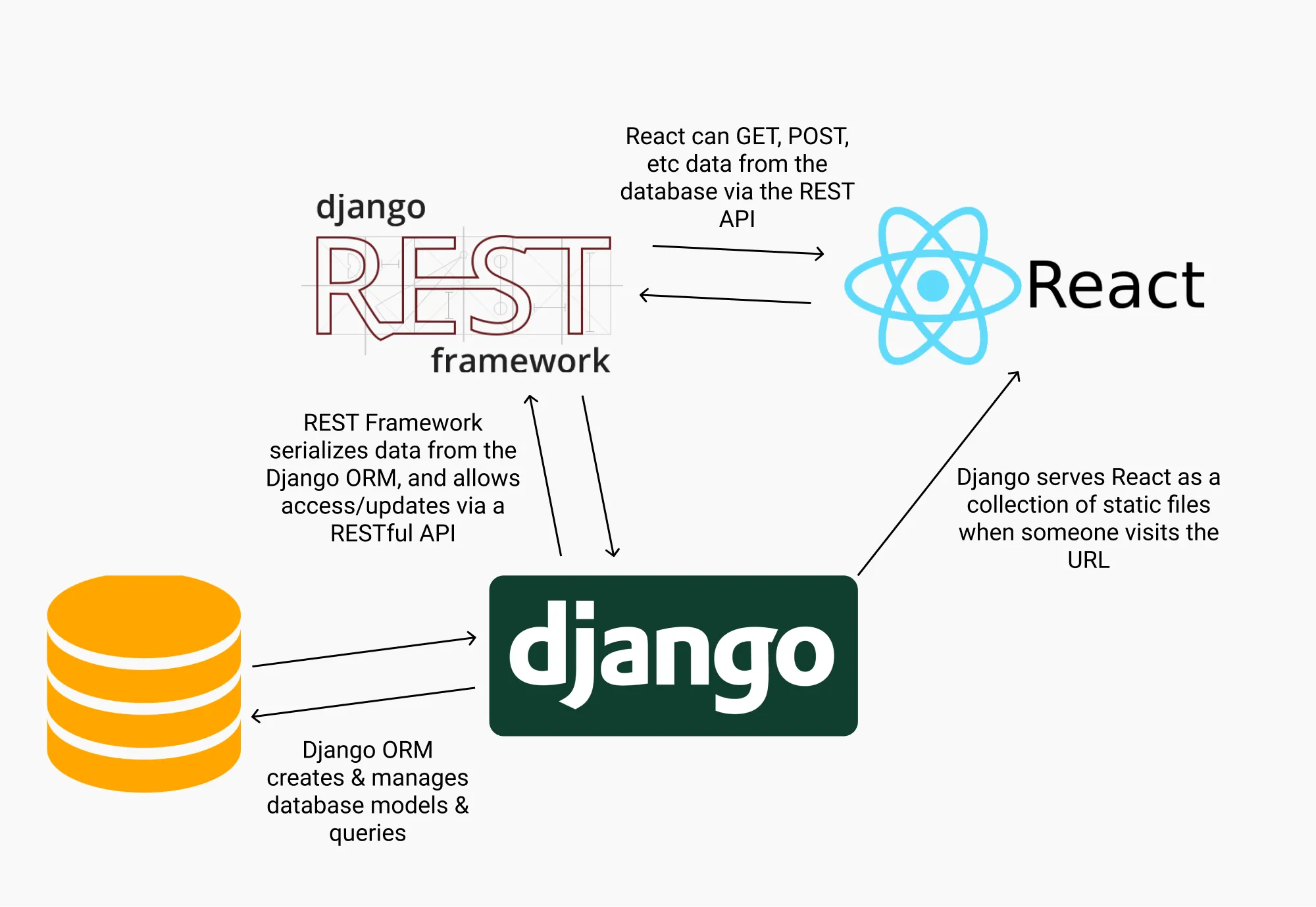
Django MVT (Model-View-Template)
Model
- Represents the data layer of the application.
- Defines the structure of the database, including tables, fields, and relationships.
- Handles data storage, retrieval, and validation.
- Interacts with the database using Django’s ORM (Object-Relational Mapper).
Define Relationships
Many-to-Many
Should be defined on either side of the relationship using ManyToManyField(). (Notice that Category was passed as a string, because the class Category was not defined yet. Django uses a string representation and it’s considered the best practice.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # One product can belongs to many categories, such as bread -> food & on_sale_product
# One category can also has many products, such as food -> bread & chicken
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
categories = models.ManyToManyField('Category')
class Category(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
|
Many-to-One
Should be defined on the many side of the relationship using ForeignKey()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| class Order(models.Model):
order_number = models.CharField(max_length=50)
customer = models.ForeignKey('Customer', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
class Customer(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
|
The kwarg: related_name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# Case 1
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
author = models.ForeignKey('Author', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
author = Author.objects.all(name='Zheng Yuan')
books = author.book_set.all()
# Default method <class_lowercase>_set
# Case 2
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
author = models.ForeignKey('Author',
related_name='books',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
books = author.books.all()
# Now, the method becomes the value of related_name
|
One-to-One
Should be defined on either side of the relationship using OneToOneField()
View
- Acts as the business logic layer.
- Processes user requests, interacts with the Model to fetch or manipulate data, and prepares the data for rendering.
- Returns a (Django’s)
HttpResponse, often by rendering a template with the processed data. - In Django, views are typically Python functions or classes.
Template
- Represents the presentation layer.
- Defines how the data is displayed to the user.
- Uses Django’s template language to dynamically generate HTML by combining static content with data from the View.
- Separates the design (HTML/CSS) from the logic (Python code).
Miscellaneous
Abstract Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class AbstractCorporation(models.Model):
# id = models.UUIDField(primary_key=True, default=uuid.uuid4, editable=False)
name = models.CharField(max_length=255, unique=True)
class Meta:
abstract = True
def __str__(self):
return self.name
|
- When defining
abstrat = True in the subclass Meta, no table will be created in the database.
Wagtail CMS
Create SnippetViewSet in <app_name>/views.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| from wagtail.snippets.views.snippets import SnippetViewSet, SnippetViewSetGroup
from corp_wechat.models import CorpWechat
from .models import Notificator
class CorpWechatSnippetViewSet(SnippetViewSet):
model = CorpWechat
form_class = CorpWechatForm
icon = "folder-open-inverse"
menu_label = 'CorpWechat'
inspect_view_enabled = True
class NotificatorSnippetViewSet(SnippetViewSet):
model = Notificator
form_fields = ['name', 'secret', 'corp']
icon = "folder-open-inverse"
menu_label = 'Notificator'
inspect_view_enabled = True
class CorpWechatSnippetViewSetGroup(SnippetViewSetGroup):
items = (CorpWechatSnippetViewSet, NotificatorSnippetViewSet)
icon = "crocodile"
menu_label = "CorpWeChat"
inspect_view_enabled = True
add_to_admin_menu = True
|
Register SnippetViewSet in <app_name>/wagtail_hooks.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| from wagtail import hooks
from .views import CorpWechatSnippetViewSetGroup
@hooks.register("register_admin_viewset")
def register_viewset():
return CorpWechatSnippetViewSetGroup()
|
Celery with Wagtail
Install Broker (macOS)
On MacOS
1
2
| $ brew install rabbitmq
$ brew services start rabbitmq
|
On Ubuntu
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| $ sudo apt-get install rabbitmq-server -y --fix-missing
$ sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server
$ sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
$ sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server
$ sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
|
Install Python Libs
1
| $ pip install celery django_celery_beat django_celery_results wagtail_celery_beat
|
Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| # EMS/settings/base.py`
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# ... other apps
"django_celery_beat",
"django_celery_results",
"wagtail_celery_beat",
]
CELERY_BROKER_URL = 'amqp://localhost:5672'
CELERY_TIMEZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
CELERY_TASK_TRACK_STARTED = True
CELERY_BEAT_SCHEDULER = "django_celery_beat.schedulers:DatabaseScheduler"
|
Make Migrations
1
2
3
4
| python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py collectstatic
|
Start Celery (In Dev)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| # In Terminal 1
$ export DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=EMS.settings.dev
$ celery -A EMS worker -l INFO
-------------- celery@Zhengs-MacBook-Air.local v5.5.0 (immunity)
--- ***** -----
-- ******* ---- macOS-15.4-arm64-arm-64bit-Mach-O 2025-04-07 18:39:09
- *** --- * ---
- ** ---------- [config]
- ** ---------- .> app: EMS:0x102debb60
- ** ---------- .> transport: amqp://guest:**@localhost:5672//
- ** ---------- .> results: disabled://
- *** --- * --- .> concurrency: 8 (prefork)
-- ******* ---- .> task events: OFF (enable -E to monitor tasks in this worker)
--- ***** -----
-------------- [queues]
.> celery exchange=celery(direct) key=celery
[tasks]
. zoom_manager.tasks.refresh_all_tokens
. zoom_manager.tasks.refresh_single_token
[2025-04-07 18:39:09,929: INFO/MainProcess] Connected to amqp://guest:**@127.0.0.1:5672//
[2025-04-07 18:39:09,934: INFO/MainProcess] mingle: searching for neighbors
[2025-04-07 18:39:10,953: INFO/MainProcess] mingle: all alone
[2025-04-07 18:39:10,966: INFO/MainProcess] celery@Zhengs-MacBook-Air.local ready.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # In Terminal 2
$ export DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=EMS.settings.dev
$ celery -A EMS beat -l INFO
celery beat v5.5.0 (immunity) is starting.
__ - ... __ - _
LocalTime -> 2025-04-07 18:40:13
Configuration ->
. broker -> amqp://guest:**@localhost:5672//
. loader -> celery.loaders.app.AppLoader
. scheduler -> django_celery_beat.schedulers.DatabaseScheduler
. logfile -> [stderr]@%INFO
. maxinterval -> 5.00 seconds (5s)
[2025-04-07 18:40:13,322: INFO/MainProcess] beat: Starting...
|
Python Scripts
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # EMS/celery.py
import os
from celery import Celery
# Set the default DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable for the celery command-line program.
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'EMS.settings')
app = Celery('EMS', include='zoom_manager.tasks')
# Add the Django settings module as a configuration source for Celery
app.config_from_object('django.conf:settings', namespace='CELERY')
app.autodiscover_tasks()
# @app.task(bind=True)
# def debug_task(self):
# print(f"Celery worker using settings file: {os.environ.get('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE')}")
# print(f'Request: {self.request!r}')
|
1
2
3
4
5
| # EMS/__init__.py
from .celery import app as celery_app
__all__ = ('celery_app',)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| # zoom_manager/tasks.py
from datetime import timedelta
import logging
from celery import shared_task
from django.utils import timezone
from django.db import connection
from .models import ZoomOAuth
from .utils import ZoomAuthenticator
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@shared_task
def refresh_single_token(zoom_oauth_id):
try:
connection.close()
connection.ensure_connection()
zoom_oauth = ZoomOAuth.objects.get(id=zoom_oauth_id)
authenticator = ZoomAuthenticator(
client_id=zoom_oauth.client_id,
client_secret=zoom_oauth.client_secret,
account_id=zoom_oauth.account_id
)
result_json = authenticator.get_access_token()
if result_json:
zoom_oauth.access_token = result_json['access_token']
zoom_oauth.access_token_expires = timezone.now() + timedelta(seconds=result_json['expires_in'])
zoom_oauth.access_token_last_updated = timezone.now()
zoom_oauth.save()
logger.info(f'Refreshed Zoom access token for {zoom_oauth.email}.')
else:
logger.error(f'Failed to refresh Zoom access token for {zoom_oauth.email}.')
except ZoomOAuth.DoesNotExist:
logger.error(f'ZoomOAuth with ID {zoom_oauth_id} not found.')
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f'Unexpected error refreshing Zoom access token (ID: {zoom_oauth_id}): {e}')
@shared_task
def refresh_all_tokens():
try:
connection.close()
connection.ensure_connection()
active_accounts = ZoomOAuth.objects.filter(
access_token_expires__gt=timezone.now() - timedelta(hours=1)
)
for account in active_accounts:
refresh_single_token.delay(account.id)
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error scheduling token refreshes: {str(e)}")
return False
|
PostgreSQL
Install Dependencies
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| $ pip install psycopg
$ brew install libpq
# Create a strong password
$ openssl rand -base64 32
MwkeNjTXakMq3Fuv1PFmBL72ekQk5Ngs5RkCFSnLrAw=
|
Create PostgreSQL Docker Container
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| services:
db:
image: bitnami/postgresql:latest
container_name: ems_postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: 'Education Management System'
POSTGRES_USER: 'postgres'
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: 'MwkeNjTXakMq3Fuv1PFmBL72ekQk5Ngs5RkCFSnLrAw='
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
ports:
- '5432:5432'
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD-SHELL', 'pg_isready -U postgres']
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
volumes:
postgres_data:
|
Config Django/Wagtail
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| DATABASES = {
# "default": {
# "ENGINE": "django.db.backends.sqlite3",
# "NAME": os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "db.sqlite3"),
# }
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': 'Education Management System',
'USER': 'postgres',
'PASSWORD': 'MwkeNjTXakMq3Fuv1PFmBL72ekQk5Ngs5RkCFSnLrAw=',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': '5432',
}
}
|
Reference
Wagtail Steps
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| pip install wagtail
mkdir directory_name
wagtail start project_name directory_name
cd directory_name
python manage.py startapp user
|
1
2
3
4
| python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserver
|