Nerve Fiber
Types of Nerve Fiber
| Classification | Type | Subtype | Example | Relative Diameter | Myelination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory & Motor |
A | \(\alpha\) | \(\alpha\) motor neurons | Large | Heavily myelinated |
| \(\beta\) | touch, pressure | Medium | Heavily myelinated | ||
| \(\gamma\) | intrafusal fibers | Medium | Heavily myelinated | ||
| \(\delta\) | touch, pressure, temperature, fast pain |
Small | Heavily myelinated | ||
| B | Small | Lightly myelinated | |||
| C | Small | Unmyelinated | |||
| Sensory | I | a | Muscle spindle afferents | Large | Myelinated |
| b | Golgi tendon organ afferents |
Large | Myelinated | ||
| II | secondary afferents of muscle spindles; touch, pressure |
Medium | Myelinated | ||
| III | touch, pressure, fast pain, temperature |
Small | Myelinated | ||
| IV | pain, temperature, olfactory |
Small | Unmyelinated |
Spinal Cord Nerve Fiber
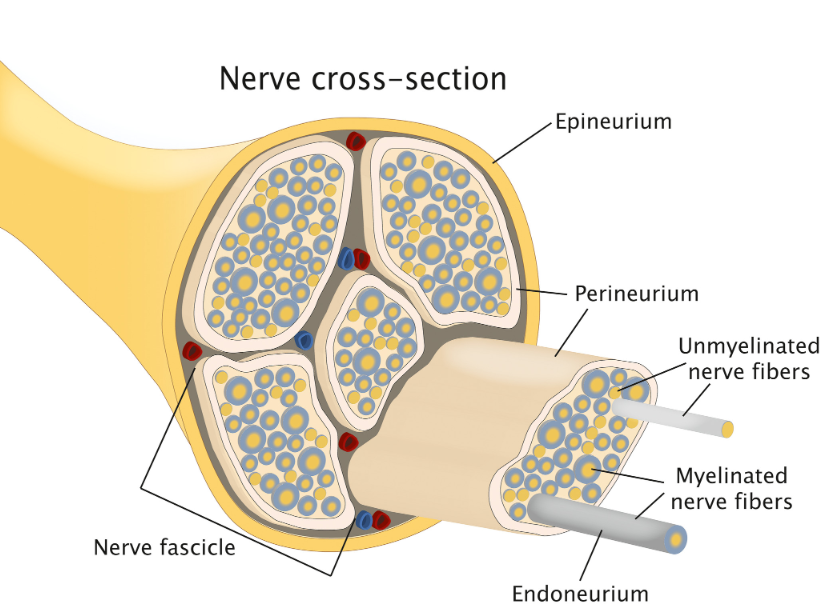 Schematic of the histologic structure of a peripheral nerve. Adapted from (Schmitd et al., 2021)
Schematic of the histologic structure of a peripheral nerve. Adapted from (Schmitd et al., 2021)
| Diameter(mm) | Number of nerve fibers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment | Ventral root (Motor) |
Dorsal root (Sensory) |
Ventral root (Motor) |
Dorsal root (Sensory) |
| C1 | 0.97±0.16 | 1.21±0.28 | 2751±639 | 6430±1606 |
| C2 | 1.34±0.30 | 2.61±0.51 | 3116±724 | 11947±2977 |
| C3 | 0.80±0.23 | 2.87±0.52 | 2460±471 | 21876±1916 |
| C4 | 1.39±0.24 | 2.49±0.34 | 3833±408 | 10647±887 |
| C5 | 2.50±0.55 | 3.43±0.77 | 7841±1020 | 23300±2856 |
| C6 | 2.23±0.73 | 3.99±0.75 | 7048±1157 | 36353±7451 |
| C7 | 2.22±0.50 | 4.61±0.87 | 8467±1019 | 39653±8458 |
| C8 | 1.71±0.60 | 3.92±0.62 | 5883±1000 | 31156±8273 |
| T1 | 1.03±0.23 | 2.18±0.31 | 5788±1186 | 26507±7617 |
| T2 | 0.75±0.11 | 1.30±0.14 | 3576±398 | 10234±1728 |
| T3 | 0.78±0.10 | 1.35±0.16 | 5499±1126 | 14888±2514 |
| T4 | 0.77±0.17 | 1.13±0.13 | 5485±973 | 10849±1832 |
| T5 | 0.64±0.08 | 1.21±0.30 | 5326±1314 | 8355±1390 |
| T6 | 0.71±0.18 | 1.07±0.16 | 3666±1407 | 10015±1666 |
| T7 | 0.78±0.15 | 1.25±0.27 | 4297±1130 | 9123±1178 |
| T8 | 0.83±0.25 | 1.29±0.18 | 3643±1340 | 7619±903 |
| T9 | 0.81±0.15 | 1.33±0.25 | 5209±704 | 8369±967 |
| T10 | 0.72±0.08 | 1.27±0.15 | 5269±963 | 11329±2724 |
| T11 | 0.69±0.08 | 1.26±0.16 | 4870±895 | 9713±1824 |
| T12 | 0.76±0.14 | 1.45±0.19 | 6538±892 | 10420±802 |
| L1 | 0.81±0.07 | 1.55±0.28 | 5384±833 | 16820±3456 |
| L2 | 0.96±0.16 | 1.93±0.27 | 7374±720 | 18615±±3284 |
| L3 | 1.19±0.07 | 2.24±0.30 | 9169±1160 | 26191±2772 |
| L4 | 1.04±0.07 | 2.48±0.38 | 7878±1386 | 31175±2686 |
| L5 | 1.37±0.16 | 2.66±0.40 | 8657±1396 | 34455±2740 |
| S1 | 1.43±0.16 | 2.95±0.57 | 8253±1419 | 41543±3036 |
| S2 | 0.93±0.11 | 2.02±0.53 | 4766±1035 | 18642±1716 |
| S3 | 0.55±0.07 | 1.32±0.60 | 2233±299 | 11971±964 |
| S4 | 0.34±0.03 | 0.52±0.17 | 1356±193 | 3402±304 |
| S5 | 0.14±0.02 | 0.27±0.13 | 906±111 | 2206±197 |
*Table adapted from (Liu et al., 2015).
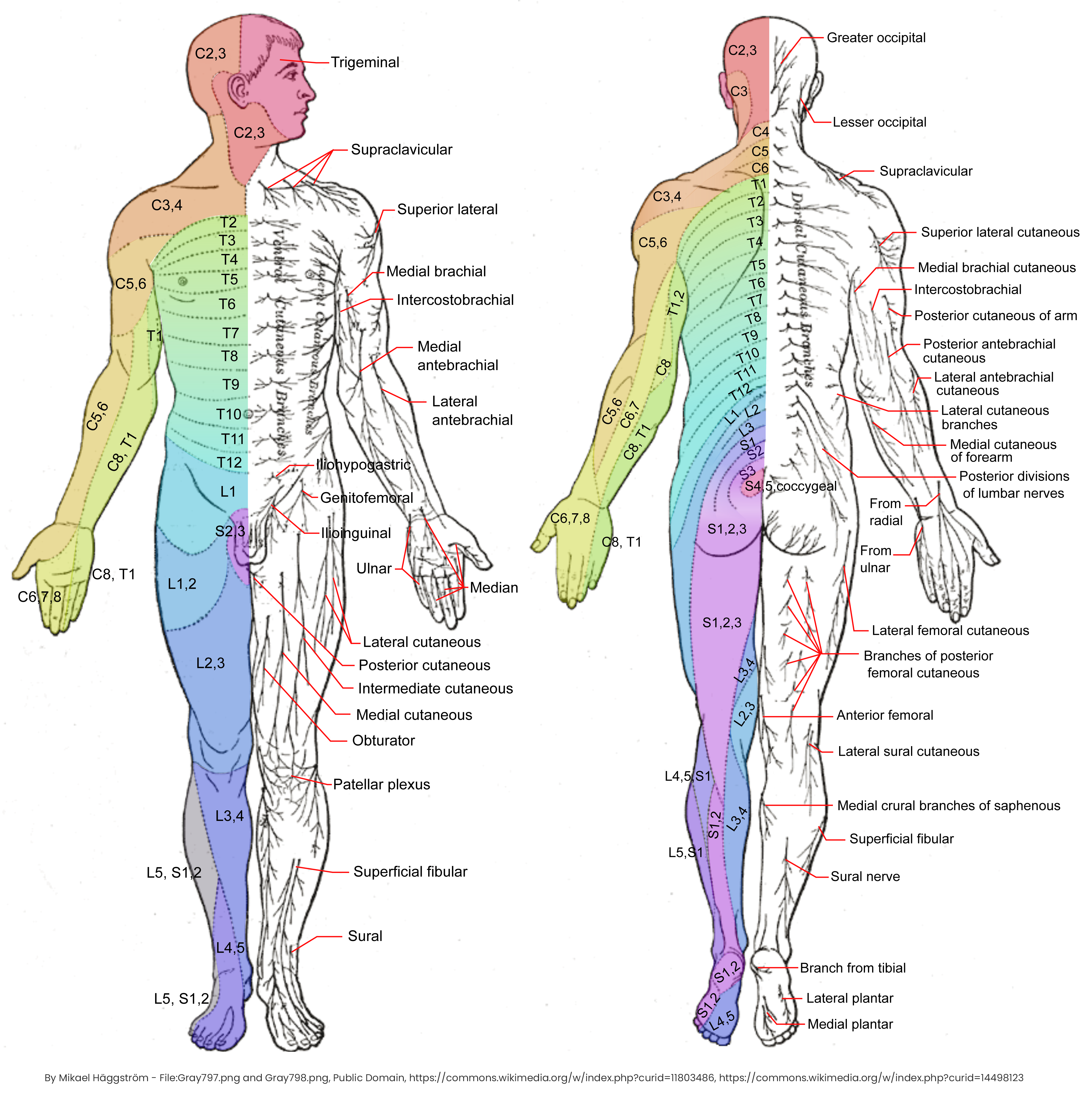 Dermatomes and Cutaneous Nerves (Wikipedia)
Dermatomes and Cutaneous Nerves (Wikipedia)
Optic Nerve Fibers
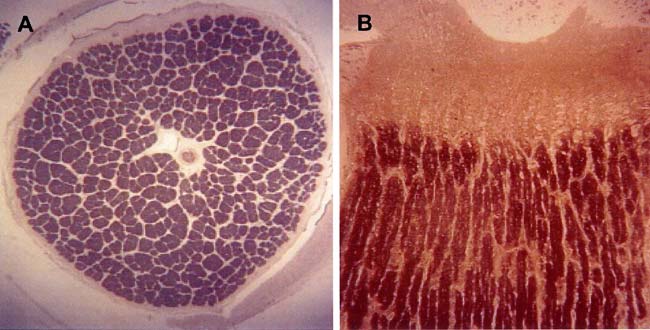 Image adapted from (Bose et al., 2005)
Image adapted from (Bose et al., 2005)
- Axon diameter: Mean=\(0.683 \mu m\), SD=\(0.369 \mu m\), SEM=\(0.026 \mu m\)
- Fig A: Normal human left optic never fiber cross-section (about 1million retinal ganglion cell axons).
- Fig B: Transverse section.
Miscellaneous
Lower Bound of Axon Diameter
Axon diameters are pushed toward the channel-noise limit of \(0.1 \mu m\) (mature neurons) due to Spontaneous Action Potentials (SAPs) (Faisal et al., 2005).
Thickness of the Cell Membrane
\(7.5 - 10 nm\) (Elert, 2023).
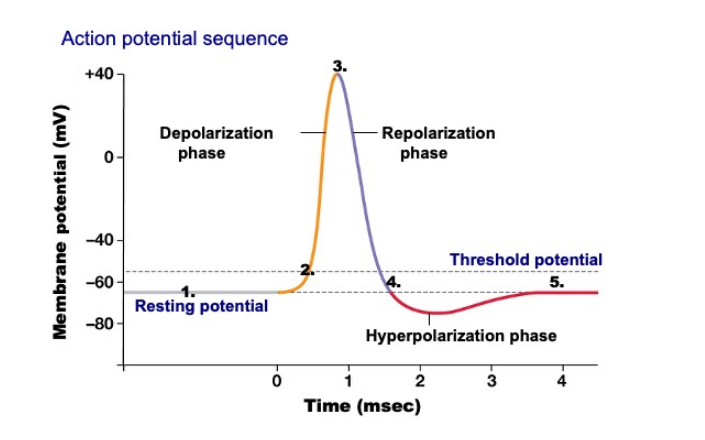
Depolarisation and Hyperpolarization Voltage
| Phase | Voltage | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Depolarization | 110mv | 1ms |
| Repolarization | 110mv | 2~3ms |
| Hyperpolarization | 5mv | 1ms |
| Refractory Period | / | 2~3ms |
Firing Rate
From \(<1Hz\) to \(200Hz\) (minimum \(5ms/spike\)).
Axonal Conduction Velocity
From \(0.1m/s\) (unmyelinated) to \(200m/s\) (myelinated) (DeMaegd et al., 2017).
Endocytosis Size Limit
Max 500nm spheres in diameter - energy-dependent process (Rejman et al., 2004).
3nm Process
| Samsung | TSMC | |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor type | MBCFET | FinFET |
| Transistor density (MTr/mm2) | 150 | 197 (theoretical) 183 (A17 Pro) |
| SRAM bit-cell size (μm2) | Unknown | 0.0199 |
| Transistor gate pitch (nm) | 40 | 45 |
Transistor density: \(197\times 10^8 Tr/mm^2 = 197 \times 10^8 \div 1000^2 = 19700 Tr/{\mu m}^2\)
Cross-section area of a matured neuron (\(d=0.1 \mu m = 100 nm)\): \(3.14 \times 0.05^2 = 0.00785 {\mu m}^2\)
The number of transistors that can be fitted into the cross-section: 154 (upper bound)
Minimum transistor thickness: 0.34 nm (reference)
Size of multi-walled carbon nanotube: \(10-40nm, 5-20 \mu m\) (Abdallah et al., 2020).
Reference
- Abdallah, B., Elhissi, A. M. A., Ahmed, W., & Najlah, M. (2020). Carbon nanotubes drug delivery system for cancer treatment. In Advances in Medical and Surgical Engineering (pp. 313–332). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819712-7.00016-4
- Bose, S., Dhillon, N., Ross-Cisneros, F. N., & Carelli, V. (2005). Relative post-mortem sparing of afferent pupil fibers in a patient with 3460 Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 243, 1175–1179.
- DeMaegd, M. L., Städele, C., & Stein, W. (2017). Axonal conduction velocity measurement. Bio-Protocol, 7(5), e2152–e2152.
- Elert, G. (2023). The Physics Factbook. https://hypertextbook.com/facts/2001/JenniferShloming.shtml
- Faisal, A. A., White, J. A., & Laughlin, S. B. (2005). Ion-channel noise places limits on the miniaturization of the brain’s wiring. Curr. Biol., 15(12), 1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.056
- Liu, Y. T., Zhou, X. J., Ma, J., Ge, Y. B., & Cao, X. (2015). The diameters and number of nerve fibers in spinal nerve roots. J. Spinal Cord Med., 38(4), 532. https://doi.org/10.1179/1079026814Z.000000000273
- Rejman, J., Oberle, V., Zuhorn, I. S., & Hoekstra, D. (2004). Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J., 377(Pt 1), 159. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20031253
- Schmitd, L. B., Perez-Pacheco, C., & D’Silva, N. J. (2021). Nerve density in cancer: Less is better. FASEB BioAdvances, 3(10), 773.